Merchandise Description
| Model No | 6301 | Seals Type | Open,Plain,Z,RS |
| FEATURE | Low Noise,Low Vibration,Long Life,High Speed | Quality Grade | Z1,V1,Z2,V2,Z3,V3 |
| Clearance | C2,C0,C3,C4 | Ball Grade | Steel Ball G16,G10 |
| Cage Material | Steel or Nylon | Corner | Normal or Black |
| OEM | Acceptable | Main Markets | India,Russia,Vietnam Korea |
| Size | 12*37*12 | Tradmark | DUZ or customer needs |
| Transport Package | Single Box or Industrial Packing | Specification | GCR15 |
| Origin | Shandong China | HS Code | 8482102000 |
###
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6000 | 10 | 0.3937 | 26 | 1.0236 | 8 | 0.315 | 4.55 | 1.95 | 7 | 4.763 | 29000 | 34000 |
| 6001 | 12 | 0.4724 | 28 | 1.1024 | 8 | 0.315 | 5.1 | 2.39 | 8 | 4.763 | 26000 | 30000 |
| 6002 | 15 | 0.5906 | 32 | 1.2598 | 9 | 0.3543 | 5.6 | 2.84 | 9 | 4.763 | 22000 | 26000 |
| 6003 | 17 | 0.6693 | 35 | 1.378 | 10 | 0.3937 | 6.8 | 3.35 | 10 | 4.763 | 20000 | 24000 |
| 6004 | 20 | 0.7874 | 42 | 1.6535 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.4 | 5.05 | 9 | 6.35 | 18000 | 21000 |
| 6005 | 25 | 0.9843 | 47 | 1.8504 | 12 | 0.4724 | 10.1 | 5.85 | 10 | 6.35 | 15000 | 18000 |
| 6006 | 30 | 1.1811 | 55 | 2.1654 | 13 | 0.5118 | 13.2 | 8.3 | 11 | 7.144 | 13000 | 15000 |
| 6007 | 35 | 1.378 | 62 | 2.4409 | 14 | 0.5512 | 16 | 10.3 | 11 | 7.938 | 12000 | 14000 |
| 6008 | 40 | 1.5748 | 68 | 2.6772 | 15 | 0.5906 | 16.8 | 11.5 | 12 | 7.938 | 10000 | 12000 |
| 6009 | 45 | 1.7717 | 75 | 2.9528 | 16 | 0.6299 | 21 | 15.1 | 12 | 8.731 | 9200 | 11000 |
| 6010 | 50 | 1.9685 | 80 | 3.1496 | 16 | 0.6299 | 21.8 | 16.6 | 13 | 8.731 | 8400 | 9800 |
| 6011 | 55 | 2.1654 | 90 | 3.5433 | 18 | 0.7087 | 28.3 | 21.2 | 12 | 11 | 7700 | 9000 |
| 6012 | 60 | 2.3622 | 95 | 3.7402 | 18 | 0.7087 | 29.5 | 23.2 | 13 | 11 | 7000 | 8300 |
| 6013 | 65 | 2.5591 | 100 | 3.937 | 18 | 0.7087 | 30.5 | 25.2 | 13 | 11.112 | 6500 | 7700 |
| 6014 | 70 | 2.7559 | 110 | 4.3307 | 20 | 0.7874 | 38 | 31 | 13 | 12.303 | 6100 | 7100 |
| 6015 | 75 | 2.9528 | 115 | 4.5276 | 20 | 0.7874 | 39.5 | 33.5 | 14 | 12.303 | 5700 | 6700 |
| 6016 | 80 | 3.1496 | 125 | 4.9213 | 22 | 0.8661 | 47.5 | 40 | 14 | 13.494 | 5300 | 6200 |
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6200 | 10 | 0.3937 | 30 | 1.1811 | 9 | 0.3543 | 5.1 | 2.39 | 8 | 4.763 | 25000 | 30000 |
| 6201 | 12 | 0.4724 | 32 | 1.2598 | 10 | 0.3937 | 6.1 | 2.75 | 7 | 5.953 | 22000 | 26000 |
| 6202 | 15 | 0.5906 | 35 | 1.378 | 11 | 0.4331 | 7.75 | 3.6 | 8 | 5.953 | 19000 | 23000 |
| 6203 | 17 | 0.6693 | 40 | 1.5748 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.6 | 4.6 | 8 | 6.747 | 18000 | 21000 |
| 6204 | 20 | 0.7874 | 47 | 1.8504 | 14 | 0.5512 | 12.8 | 6.65 | 8 | 7.938 | 16000 | 18000 |
| 6205 | 25 | 0.9843 | 52 | 2.0472 | 15 | 0.5906 | 14 | 7.85 | 9 | 7.938 | 13000 | 15000 |
| 6206 | 30 | 1.1811 | 62 | 2.4409 | 16 | 0.6299 | 19.5 | 11.3 | 9 | 9.525 | 11000 | 13000 |
| 6207 | 35 | 1.378 | 72 | 2.8346 | 17 | 0.6693 | 25.7 | 15.3 | 9 | 11.112 | 9800 | 11000 |
| 6208 | 40 | 1.5748 | 80 | 3.1496 | 18 | 0.7087 | 29.1 | 17.8 | 9 | 12 | 8700 | 10000 |
| 6209 | 45 | 1.7717 | 85 | 3.3465 | 19 | 0.748 | 32.5 | 20.4 | 10 | 12 | 7800 | 9200 |
| 6210 | 50 | 1.9685 | 90 | 3.5433 | 20 | 0.7874 | 35 | 23.2 | 10 | 12.7 | 7100 | 8300 |
| 6211 | 55 | 2.1654 | 100 | 3.937 | 21 | 0.8268 | 43.5 | 29.2 | 10 | 14.288 | 6400 | 7600 |
| 6212 | 60 | 2.3622 | 110 | 4.3307 | 22 | 0.8661 | 52.5 | 36 | 10 | 15.081 | 6000 | 7000 |
| 6213 | 65 | 2.5591 | 120 | 4.7244 | 23 | 0.9055 | 57.5 | 40 | 10 | 16.669 | 5500 | 6500 |
| 6214 | 70 | 2.7559 | 125 | 4.9213 | 24 | 0.9449 | 62 | 44 | 11 | 16.462 | 5100 | 6000 |
| 6215 | 75 | 2.9528 | 130 | 5.1181 | 25 | 0.9843 | 66 | 49.5 | 11 | 17.462 | 4800 | 5600 |
| 6216 | 80 | 3.1496 | 140 | 5.5118 | 26 | 1.0236 | 72.5 | 53 | 11 | 18.256 | 4500 | 5300 |
| 6217 | 85 | 3.3465 | 150 | 5.9055 | 28 | 1.1024 | 83.5 | 64 | 11 | 19.844 | 4200 | 5000 |
| 6218 | 90 | 3.5433 | 160 | 6.2992 | 30 | 1.1811 | 96 | 71.5 | 10 | 22.225 | 4000 | 4700 |
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6300 | 10 | 0.3937 | 35 | 1.378 | 11 | 0.4331 | 8.2 | 3.5 | 6 | 7.144 | 23000 | 27000 |
| 6301 | 12 | 0.4724 | 37 | 1.4567 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.7 | 4.2 | 6 | 7.938 | 20000 | 24000 |
| 6302 | 15 | 0.5906 | 42 | 1.6535 | 13 | 0.5118 | 11.4 | 5.45 | 7 | 7.938 | 17000 | 21000 |
| 6303 | 17 | 0.6693 | 47 | 1.8504 | 14 | 0.5512 | 13.5 | 6.55 | 7 | 8.731 | 16000 | 19000 |
| 6304 | 20 | 0.7874 | 52 | 2.0472 | 15 | 0.5906 | 15.9 | 7.9 | 7 | 9.525 | 14000 | 27000 |
| 6305 | 25 | 0.9843 | 62 | 2.4409 | 17 | 0.6693 | 21.2 | 10.9 | 7 | 11.5 | 12000 | 14000 |
| 6306 | 30 | 1.1811 | 72 | 2.8346 | 19 | 0.748 | 26.7 | 15 | 8 | 12 | 10000 | 12000 |
| 6307 | 35 | 1.378 | 80 | 3.1496 | 21 | 0.8268 | 33.5 | 19.1 | 8 | 13.494 | 8800 | 10000 |
| 6308 | 40 | 1.5748 | 90 | 3.5433 | 23 | 0.9055 | 40.5 | 24 | 8 | 15.081 | 7800 | 9200 |
| 6309 | 45 | 1.7717 | 100 | 3.937 | 25 | 0.9843 | 53 | 32 | 8 | 17.462 | 7000 | 8200 |
| 6310 | 50 | 1.9685 | 110 | 4.3307 | 27 | 1.063 | 62 | 38.5 | 8 | 19.05 | 6400 | 7500 |
| 6311 | 55 | 2.1654 | 120 | 4.7244 | 29 | 1.1417 | 71.5 | 45 | 8 | 20.638 | 5800 | 6800 |
| 6312 | 60 | 2.3622 | 130 | 5.1181 | 31 | 1.2205 | 82 | 52 | 8 | 22.225 | 5400 | 6300 |
| 6313 | 65 | 2.5591 | 140 | 5.5118 | 33 | 1.2992 | 92.5 | 60 | 8 | 24 | 4900 | 5800 |
| 6314 | 70 | 2.7559 | 150 | 5.9055 | 35 | 1.378 | 104 | 68 | 8 | 25.4 | 4600 | 5400 |
| 6315 | 75 | 2.9528 | 160 | 6.2992 | 37 | 1.4567 | 113 | 77 | 8 | 26.988 | 4300 | 5000 |
| 6316 | 80 | 3.1496 | 170 | 6.6929 | 39 | 1.5354 | 123 | 86.5 | 8 | 28.575 | 4000 | 4700    |
| Model No | 6301 | Seals Type | Open,Plain,Z,RS |
| FEATURE | Low Noise,Low Vibration,Long Life,High Speed | Quality Grade | Z1,V1,Z2,V2,Z3,V3 |
| Clearance | C2,C0,C3,C4 | Ball Grade | Steel Ball G16,G10 |
| Cage Material | Steel or Nylon | Corner | Normal or Black |
| OEM | Acceptable | Main Markets | India,Russia,Vietnam Korea |
| Size | 12*37*12 | Tradmark | DUZ or customer needs |
| Transport Package | Single Box or Industrial Packing | Specification | GCR15 |
| Origin | Shandong China | HS Code | 8482102000 |
###
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6000 | 10 | 0.3937 | 26 | 1.0236 | 8 | 0.315 | 4.55 | 1.95 | 7 | 4.763 | 29000 | 34000 |
| 6001 | 12 | 0.4724 | 28 | 1.1024 | 8 | 0.315 | 5.1 | 2.39 | 8 | 4.763 | 26000 | 30000 |
| 6002 | 15 | 0.5906 | 32 | 1.2598 | 9 | 0.3543 | 5.6 | 2.84 | 9 | 4.763 | 22000 | 26000 |
| 6003 | 17 | 0.6693 | 35 | 1.378 | 10 | 0.3937 | 6.8 | 3.35 | 10 | 4.763 | 20000 | 24000 |
| 6004 | 20 | 0.7874 | 42 | 1.6535 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.4 | 5.05 | 9 | 6.35 | 18000 | 21000 |
| 6005 | 25 | 0.9843 | 47 | 1.8504 | 12 | 0.4724 | 10.1 | 5.85 | 10 | 6.35 | 15000 | 18000 |
| 6006 | 30 | 1.1811 | 55 | 2.1654 | 13 | 0.5118 | 13.2 | 8.3 | 11 | 7.144 | 13000 | 15000 |
| 6007 | 35 | 1.378 | 62 | 2.4409 | 14 | 0.5512 | 16 | 10.3 | 11 | 7.938 | 12000 | 14000 |
| 6008 | 40 | 1.5748 | 68 | 2.6772 | 15 | 0.5906 | 16.8 | 11.5 | 12 | 7.938 | 10000 | 12000 |
| 6009 | 45 | 1.7717 | 75 | 2.9528 | 16 | 0.6299 | 21 | 15.1 | 12 | 8.731 | 9200 | 11000 |
| 6010 | 50 | 1.9685 | 80 | 3.1496 | 16 | 0.6299 | 21.8 | 16.6 | 13 | 8.731 | 8400 | 9800 |
| 6011 | 55 | 2.1654 | 90 | 3.5433 | 18 | 0.7087 | 28.3 | 21.2 | 12 | 11 | 7700 | 9000 |
| 6012 | 60 | 2.3622 | 95 | 3.7402 | 18 | 0.7087 | 29.5 | 23.2 | 13 | 11 | 7000 | 8300 |
| 6013 | 65 | 2.5591 | 100 | 3.937 | 18 | 0.7087 | 30.5 | 25.2 | 13 | 11.112 | 6500 | 7700 |
| 6014 | 70 | 2.7559 | 110 | 4.3307 | 20 | 0.7874 | 38 | 31 | 13 | 12.303 | 6100 | 7100 |
| 6015 | 75 | 2.9528 | 115 | 4.5276 | 20 | 0.7874 | 39.5 | 33.5 | 14 | 12.303 | 5700 | 6700 |
| 6016 | 80 | 3.1496 | 125 | 4.9213 | 22 | 0.8661 | 47.5 | 40 | 14 | 13.494 | 5300 | 6200 |
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6200 | 10 | 0.3937 | 30 | 1.1811 | 9 | 0.3543 | 5.1 | 2.39 | 8 | 4.763 | 25000 | 30000 |
| 6201 | 12 | 0.4724 | 32 | 1.2598 | 10 | 0.3937 | 6.1 | 2.75 | 7 | 5.953 | 22000 | 26000 |
| 6202 | 15 | 0.5906 | 35 | 1.378 | 11 | 0.4331 | 7.75 | 3.6 | 8 | 5.953 | 19000 | 23000 |
| 6203 | 17 | 0.6693 | 40 | 1.5748 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.6 | 4.6 | 8 | 6.747 | 18000 | 21000 |
| 6204 | 20 | 0.7874 | 47 | 1.8504 | 14 | 0.5512 | 12.8 | 6.65 | 8 | 7.938 | 16000 | 18000 |
| 6205 | 25 | 0.9843 | 52 | 2.0472 | 15 | 0.5906 | 14 | 7.85 | 9 | 7.938 | 13000 | 15000 |
| 6206 | 30 | 1.1811 | 62 | 2.4409 | 16 | 0.6299 | 19.5 | 11.3 | 9 | 9.525 | 11000 | 13000 |
| 6207 | 35 | 1.378 | 72 | 2.8346 | 17 | 0.6693 | 25.7 | 15.3 | 9 | 11.112 | 9800 | 11000 |
| 6208 | 40 | 1.5748 | 80 | 3.1496 | 18 | 0.7087 | 29.1 | 17.8 | 9 | 12 | 8700 | 10000 |
| 6209 | 45 | 1.7717 | 85 | 3.3465 | 19 | 0.748 | 32.5 | 20.4 | 10 | 12 | 7800 | 9200 |
| 6210 | 50 | 1.9685 | 90 | 3.5433 | 20 | 0.7874 | 35 | 23.2 | 10 | 12.7 | 7100 | 8300 |
| 6211 | 55 | 2.1654 | 100 | 3.937 | 21 | 0.8268 | 43.5 | 29.2 | 10 | 14.288 | 6400 | 7600 |
| 6212 | 60 | 2.3622 | 110 | 4.3307 | 22 | 0.8661 | 52.5 | 36 | 10 | 15.081 | 6000 | 7000 |
| 6213 | 65 | 2.5591 | 120 | 4.7244 | 23 | 0.9055 | 57.5 | 40 | 10 | 16.669 | 5500 | 6500 |
| 6214 | 70 | 2.7559 | 125 | 4.9213 | 24 | 0.9449 | 62 | 44 | 11 | 16.462 | 5100 | 6000 |
| 6215 | 75 | 2.9528 | 130 | 5.1181 | 25 | 0.9843 | 66 | 49.5 | 11 | 17.462 | 4800 | 5600 |
| 6216 | 80 | 3.1496 | 140 | 5.5118 | 26 | 1.0236 | 72.5 | 53 | 11 | 18.256 | 4500 | 5300 |
| 6217 | 85 | 3.3465 | 150 | 5.9055 | 28 | 1.1024 | 83.5 | 64 | 11 | 19.844 | 4200 | 5000 |
| 6218 | 90 | 3.5433 | 160 | 6.2992 | 30 | 1.1811 | 96 | 71.5 | 10 | 22.225 | 4000 | 4700 |
| Bearing No. | I. D | O. D | W | Loading Rating(KN) | Steel Ball Parameter | Max Speed | ||||||
| D | D | B | Dynamic | Static | No. | Size | Grease | Oil | ||||
| mm | Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Cr | Cor | mm | R/min | R/min | ||
| 6300 | 10 | 0.3937 | 35 | 1.378 | 11 | 0.4331 | 8.2 | 3.5 | 6 | 7.144 | 23000 | 27000 |
| 6301 | 12 | 0.4724 | 37 | 1.4567 | 12 | 0.4724 | 9.7 | 4.2 | 6 | 7.938 | 20000 | 24000 |
| 6302 | 15 | 0.5906 | 42 | 1.6535 | 13 | 0.5118 | 11.4 | 5.45 | 7 | 7.938 | 17000 | 21000 |
| 6303 | 17 | 0.6693 | 47 | 1.8504 | 14 | 0.5512 | 13.5 | 6.55 | 7 | 8.731 | 16000 | 19000 |
| 6304 | 20 | 0.7874 | 52 | 2.0472 | 15 | 0.5906 | 15.9 | 7.9 | 7 | 9.525 | 14000 | 27000 |
| 6305 | 25 | 0.9843 | 62 | 2.4409 | 17 | 0.6693 | 21.2 | 10.9 | 7 | 11.5 | 12000 | 14000 |
| 6306 | 30 | 1.1811 | 72 | 2.8346 | 19 | 0.748 | 26.7 | 15 | 8 | 12 | 10000 | 12000 |
| 6307 | 35 | 1.378 | 80 | 3.1496 | 21 | 0.8268 | 33.5 | 19.1 | 8 | 13.494 | 8800 | 10000 |
| 6308 | 40 | 1.5748 | 90 | 3.5433 | 23 | 0.9055 | 40.5 | 24 | 8 | 15.081 | 7800 | 9200 |
| 6309 | 45 | 1.7717 | 100 | 3.937 | 25 | 0.9843 | 53 | 32 | 8 | 17.462 | 7000 | 8200 |
| 6310 | 50 | 1.9685 | 110 | 4.3307 | 27 | 1.063 | 62 | 38.5 | 8 | 19.05 | 6400 | 7500 |
| 6311 | 55 | 2.1654 | 120 | 4.7244 | 29 | 1.1417 | 71.5 | 45 | 8 | 20.638 | 5800 | 6800 |
| 6312 | 60 | 2.3622 | 130 | 5.1181 | 31 | 1.2205 | 82 | 52 | 8 | 22.225 | 5400 | 6300 |
| 6313 | 65 | 2.5591 | 140 | 5.5118 | 33 | 1.2992 | 92.5 | 60 | 8 | 24 | 4900 | 5800 |
| 6314 | 70 | 2.7559 | 150 | 5.9055 | 35 | 1.378 | 104 | 68 | 8 | 25.4 | 4600 | 5400 |
| 6315 | 75 | 2.9528 | 160 | 6.2992 | 37 | 1.4567 | 113 | 77 | 8 | 26.988 | 4300 | 5000 |
| 6316 | 80 | 3.1496 | 170 | 6.6929 | 39 | 1.5354 | 123 | 86.5 | 8 | 28.575 | 4000 | 4700    |
Mechanical advantages of pulleys
A pulley is a mechanical device used to transmit motion. The device has a variety of uses, including lifting heavy objects. In this article, we will discuss the mechanical advantages, types, common uses and safety considerations of pulleys. We’ll also discuss how to identify pulleys and their components, and what to look out for when using pulleys. Read on to learn more about pulleys.
Mechanical advantages of pulleys
The mechanical advantage of pulleys is that they change the direction of force from one direction to another. In this way, the person lifting the heavy object can change its position with minimal effort. The pulleys are also easy to install and require no lubrication after installation. They are also relatively cheap. Combinations of pulleys and cables can be used to change the direction of the load.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system increases with the number of ropes used in the system. The more cycles a system has, the more efficient it is. If the system had only one rope, the force required to pull the weight would be equal. By adding a second rope, the effort required to pull the weight is reduced. This increase in efficiency is known as the mechanical advantage of the pulley.
Pulleys have many uses. For example, ziplines are one application. This is a good example of pulleys in use today. Pulley systems can be complex and require a lot of space. Using ziplines as an example, advanced students can calculate the mechanical advantage of multiple pulleys by dividing the work done by each pulley by the remainder or fraction. Regents at the University of Colorado created a zipline with K-12 input.
Another use for pulleys is weight lifting. This technique is very effective when using multiple strands of rope. A single rope going from one pulley to the other with just two hands is not enough to lift heavy objects. Using a pulley system will greatly increase the force you receive. This power is multiplied over a larger area. So your lifting force will be much greater than the force exerted by a single rope.
The pulley is a great invention with many uses. For example, when lifting heavy objects, pulleys are a great way to get the job done, and it’s easier to do than one person. The pulley is fixed on a hinge and rotates on a shaft or shaft. Then pull the rope down to lift the object. A pulley assembly will make the task easier. In addition, it will also allow power to be transferred from one rotary shaft to another.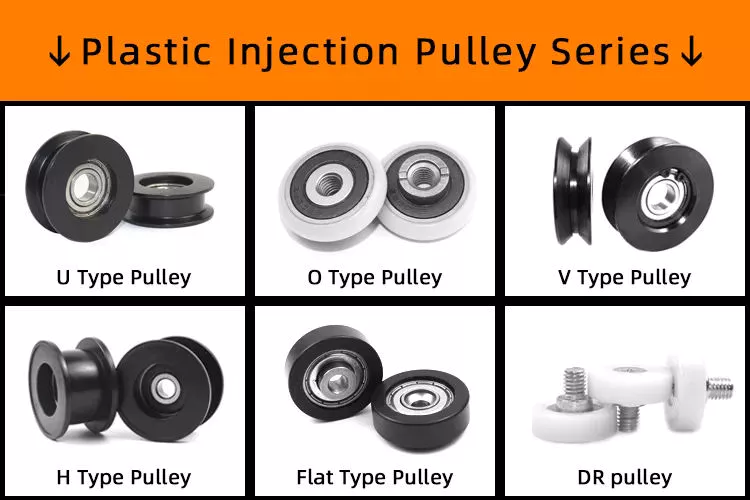
Types of pulleys
If you are an engineer, you must have come across different types of pulleys. Some pulleys come in multiple types, but a typical pulley has only one type. These types of pulleys are used in various industrial processes. Here are some common types of pulleys that engineers encounter on the job. In addition to the above, there are many more. If you haven’t seen them in practice, you can check out a list of the different types below.
Fixed pulleys: Fixed pulleys have a roller attached to a fixed point. The force required to pull the load through the fixed pulley is the same as the force required to lift the object. Movable pulleys allow you to change the direction of the force, for example, by moving it laterally. Likewise, movable pulleys can be used to move heavy objects up and down. Commonly used in multi-purpose elevators, cranes and weight lifters.
Composite pulleys combine fixed and movable pulleys. This combination adds to the mechanical advantage of both systems. It can also change the direction of the force, making it easier to handle large loads. This article discusses the different types of pulleys used for lifting and moving. Braided pulleys are an example of these pulleys. They combine the advantages of both types.
A simple pulley consists of one or more wheels, which allow it to reverse the direction of the force used to lift the load. On the other hand, dual-wheel pulleys can help lift twice the weight. By combining multiple materials into one pulley, a higher ME will be required. Regardless of the type of pulley, understanding the principles behind it is critical.
Pulleys are an important part of construction and mechanical engineering, and their use dates back to Archimedes. They are a common feature of oil derricks and escalators. The main use of pulleys is to move heavy objects such as boats. In addition to this, they are used in other applications such as extending ladders and lifting heavy objects. The pulley also controls the aircraft rudder, which is important in many different applications.
Commonly used
Common uses for pulleys are varied. Pulley systems are found throughout most areas of the house, from adjustable clotheslines to motor pulleys in different machines. Commercially, one of the most common uses is for cranes. Cranes are equipped with pulleys to lift heavy objects. It is also common to use pulley systems in tall buildings, which allow tall buildings to move with relative ease.
Pulleys are commonly used in interception and zipline systems, where a continuous rope around the pulley transmits force. Depending on the application, the rope is either light or strong. Pulleys are formed by wrapping a rope around a set of wheels. The rope pulls the object in the direction of the applied force. Some elevators use this system. Pull a cable on one end and attach a counterweight on the other end.
Another common use for pulleys is to move heavy objects. Pulleys mounted on walls, ceilings or other objects can lift heavy objects like heavy toolboxes or 2×4 planks. The device can also be used to transfer power from one rotating shaft to another. When used to lift heavy objects, pulleys can be used to help you achieve your goals of a good workout.
Pulley systems have a variety of uses, from the most basic to the most advanced. Its popularity is indisputable and it is used in different industries. A good example is timing belts. These pulleys transmit power to other components in the same direction. They can also be static or dynamic depending on the needs of the machine. In most cases, the pulley system is custom made for the job.
Pulley systems can be simple or complex, but all three systems transfer energy efficiently. In most cases, the mechanical advantage of a single pulley is 1 and the mechanical advantage of a single active pulley is 2. On the other hand, a single live pulley only doubles the force. This means you can trade effort for distance. Pulleys are the perfect solution for many common applications.
Safety Notice
If you use pulleys, you need to take some safety precautions. First, make sure you’re wearing the correct protective gear. A hard hat is a must to avoid being hit by falling objects. You may also want to wear gloves for added protection. You should also maintain a good distance from the pulley so that nearby people can walk around it safely.
Another important safety measure to take before using a chain hoist is to barricade the area to be lifted. Use marker lines to prevent the load from sliding when moving horizontally. Finally, use only the sprocket set for vertical lift. Always install shackle pins before lifting. You should also wear personal protective equipment such as earplugs and safety glasses when using the chain hoist.
In addition to these safety measures, you should also use cables made from aerospace-grade nylon. They will last many cycles and are made of high quality materials. Also, make sure the cables are lubricated. These measures reduce friction and corrosion. No matter what industry you are in, be sure to follow these precautions to ensure a long service life for your cables. Consult the cable manufacturer if you are unsure of the appropriate material. A company with 60 years of experience in the cable industry can recommend the right material for your system.

